In this article, I am going to discuss the most frequently asked SQL Server Functions Interview Questions and Answers.
What
is a function in SQL Server?
A
function is a database object in SQL Server. Basically, it is a set of SQL
statements that accept only input parameters, perform actions and return the
result. The function can return only a single value or a table. We can’t use
the function to Insert, Update and Delete records in the database
table(s).
- It
is also a subprogram like a stored procedure that is defined for
performing an action such as complex calculation and returns result of the
action as a value.
- These
functions are created by the user or programmer.
- Functions
are taking some parameters, do some processing and returning some results
back
For
example Select SQUARE(3) Output:
9
Some
functions also do not take any parameters. For Example: Select
GETDATE()
So,
we can say that a function can have the parameter that is optional but a
function should return a value that is mandatory.
Types
of User-Defined Functions in SQL Server:
In
SQL Server, there are 3 types of User-Defined Functions
- Scalar
functions
- Inline
table-valued functions
- Multi-statement
table-valued functions
What
is a scalar function in SQL Server?
The
functions which return a single value are known as scalar value function.
The Scalar functions may or may not have parameters, but
always return a single (scalar) value. The returned value can be of any data
type, except text, ntext, image, cursor, and timestamp.
To
create a function, we use the following syntax:
What is a table-valued function?
In
this case, we can return a table as an output from the function. These are
again of two types
- Inline Table-valued
Function
- Multi-statement table value function
Where can we use the Inline Table-Valued function?
The
Inline Table-Valued functions can be used to achieve the functionality of
parameterized views. The table returned by the table-valued function can also
be used in joins with other tables.
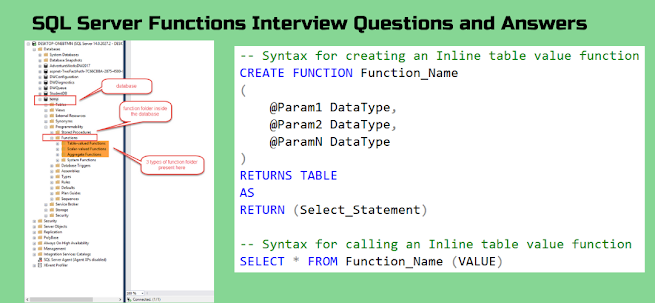
What is Inline table-valued functions?
In
this case, the body of the function will have only a single select statement
prepared with the “RETURN” statement. The syntax for creating a table value
function
CREATE/ALTER FUNCTION <FUNCTION NAME>(@<VARIABLE
NAME><DATA TYPE> [SIZE])
RETURNS TABLE
AS
RETURN <SELECT STATEMENT>
- We specify the Table as the return type instead of any scalar
data type.
- The function body is not
closed between BEGIN and END block
- The structure of the table
that gets returned is determined by the select statement within the
function.
What are Multi-Statement Table-Valued Functions in SQL Server?
This
is the same as the inline table-valued function which can return a table as an
output but here the body can contain more than one statement and also the
structure of the table being returned can be defined. The Syntax is given below
CREATE/ALTER FUNCTION <FUNCTIONNAME> (@<PARAM><DATATYPE> [SIZE].....)RETURNS @<TABLE VAR> TABLE (<COLUMN DEFINITIONS>)[WITH <FUNCTION ATTRIBUTES>]ASBEGIN <FUNCTION BODY> RETURNEND
Note: In case of a
multi-statement table-valued function we need to define our own structure to
the table being return.
Differences between Inline Table-Valued functions and
Multi-statement Table-Valued functions
In an Inline Table-Valued function, the RETURNS clause cannot
contain the structure of the table, the function returns. Whereas, with the
multi-statement table-valued function, we specify the structure of the table
that gets returned
Inline
Table-Valued function cannot have BEGIN and END block as it returns a single
select statement, whereas the multi-statement function can have the begin and
end block as it contains more than one select statement.
Inline
Table-valued functions are better for performance than multi-statement
table-valued functions. If the given task, can be achieved using an inline
table-valued function, always prefer to use them, over multi-statement
table-valued functions.
It’s
possible to update the underlying table, using an inline table-valued function,
but not possible using a multi-statement table-valued function.
Reason for improved performance
of an inline table-valued function:
Internally,
SQL Server treats an inline table-valued function much like it would a view and
treats a multi-statement table-valued function similar to how it would a stored
procedure.
What are the differences between functions and procedures in SQL
Server?
Stored
Procedures are pre-compiled objects which are compiled for the first time and
its compiled format is saved which executes (compiled code) whenever it is
called. But Function is compiled and executed every time when it is
called.
BASIC
DIFFERENCE
- The
function must return a value but in Stored Procedure, it is optional
(Procedure can return zero or n values).
- Functions
can have only input parameters whereas Procedures can have input/output
parameters.
- A
Function can be called from Procedure whereas Procedures cannot be
called from Function
- From
a procedure, we can call another procedure or a function whereas from a
function we can call another function but not a procedure.
ADVANCE
DIFFERENCE
- The
procedure allows SELECT as well as DML (INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE) statement in
it whereas Function allows only SELECT statement in it.
- Procedures
cannot be utilized in a SELECT statement whereas Function can be embedded
in a SELECT statement.
- Stored
Procedures cannot be used in the SQL statements anywhere in the
WHERE/HAVING/SELECT section whereas Function can be.
- Functions
that return tables can be treated as a row set. This can be used in JOINs
with other tables
- The
exception can be handled by a try-catch block in a procedure whereas
try-catch block cannot be used in a Function.
- We
can go for Transaction Management in Procedure whereas we can’t go into
Function.
- We
call a procedure using EXECUTE/ EXEC command whereas a function is called
by using the SELECT command only.
- Stored
procedures support deferred name resolution. For example, while writing a
stored procedure that uses table names, for example, table1, table2, etc.
but these tables do not exist in the database is allowed during the
creation of the stored procedure but runtime throws error whereas
functions do not support deferred name resolution.
In
the next article, I am going to discuss the most frequently asked SQL
Server Constraints Interview Questions and Answers. Here, in this article,
I try to explain the most frequently asked SQL Server Functions
Interview Questions and Answers. I hope you enjoy this SQL Server
Functions Interview Questions and Answers article. I would like to have your
feedback. Please post your feedback, question, or comments about this SQL
Server Functions Interview Questions and Answers article.





0 Comments